Introduction
In healthcare, effective communication is crucial for building trust, understanding, and rapport with patients and colleagues. Body language, a nonverbal form of communication, plays a significant role in the way we interact and understand each other. However, bad body language can negatively impact communication, causing misunderstandings and affecting the quality of care provided. In this article, we will explore some common examples of bad body language in healthcare and ways to detect and address them.
What is Body language?
Body language refers to the nonverbal cues and signals that people use to communicate their thoughts, emotions, and attitudes. In healthcare settings, a body language is an essential tool that can be used to reveal the secrets behind common nonverbal cues in patient care.
The role of nonverbal communication in healthcare
Nonverbal communication plays a crucial role in healthcare settings, as it can provide important clues about a patient’s mental and physical state. When patients are unable or unwilling to express themselves verbally, nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, gestures, and body posture can help healthcare professionals to better understand their needs and emotions.
For example, a patient who is clenching their jaw or furrowing their brow may be experiencing pain or discomfort, even if they do not verbalize it. A patient who avoids eye contact or slouches may be feeling depressed or anxious. By paying close attention to these nonverbal cues, healthcare professionals can provide more effective and compassionate care.
In addition to helping healthcare professionals understand their patients, nonverbal communication can also help to build trust and rapport. Patients who feel that their healthcare providers are attentive to their nonverbal cues may be more likely to feel heard and understood, which can enhance the therapeutic relationship.
Overall, the role of nonverbal communication in healthcare cannot be overstated. By learning how to read and interpret nonverbal cues, healthcare professionals can improve patient care and build stronger relationships with their patients.
Nonverbal Cues commonly used by healthcare providers
There are many types of body language that healthcare providers can use to communicate effectively with their patients. Here are 11 types of body language and how they relate to healthcare:
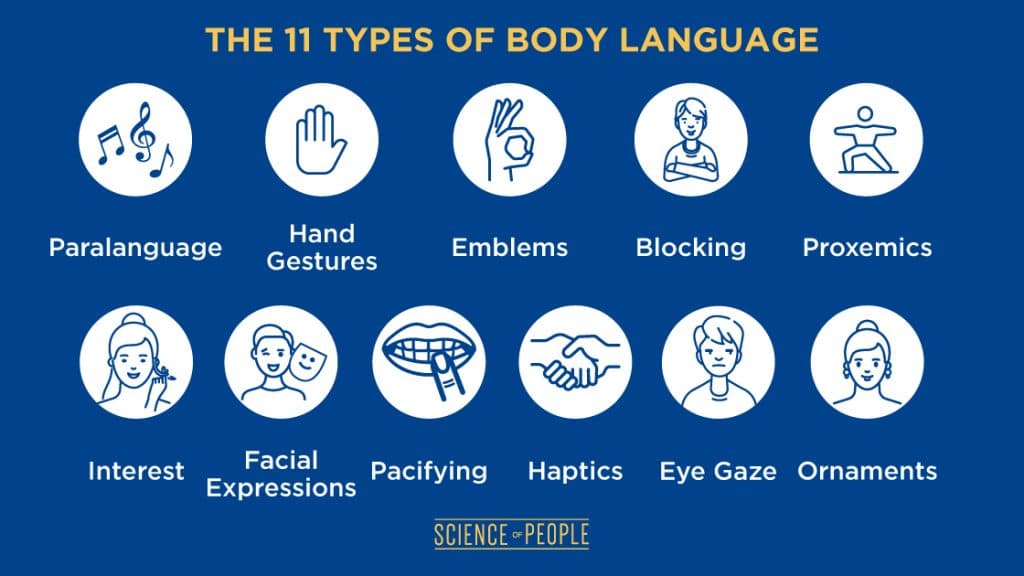
Eye contact:
Making eye contact with a patient can help to establish trust and build rapport. It shows that the healthcare provider is engaged and interested in what the patient is saying.
Facial expressions
The science of facial expressions
Facial expressions are an important aspect of nonverbal communication in healthcare settings. Research has shown that human faces are capable of producing over 10,000 unique facial expressions, each of which conveys a different emotion or message.
The science of facial expressions involves the study of how facial muscles work together to create different expressions. There are six basic facial expressions that are universally recognized across cultures: happiness, sadness, anger, surprise, fear, and disgust.
In healthcare settings, patients may display a range of facial expressions that can provide important clues about their mental and physical state. For example, a patient who is smiling and making eye contact may be feeling happy and comfortable, while a patient who is frowning and avoiding eye contact may be feeling sad or anxious.
Positive facial expressions, such as smiling or nodding, can help to put patients at ease and create a more relaxed environment. Conversely, negative facial expressions, such as frowning or scowling, can create tension and anxiety.
Different expressions can also indicate pain or discomfort. For example, a patient who is grimacing or clenching their jaw may be experiencing pain, while a patient who is rubbing their temples or forehead may be experiencing a headache.
By paying close attention to their patients’ facial expressions, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into their patients’ emotional and physical state. This can help them to provide more effective care and to build stronger, more trusting relationships with their patients.
Posture
Healthcare providers who stand or sit up straight and maintain an open stance can convey confidence and approachability. Conversely, closed postures, such as crossed arms or slouching, can indicate defensiveness or disinterest.
Touch
Appropriate touch, such as a reassuring pat on the arm or holding a patient’s hand, can convey empathy and support. However, healthcare providers should always ask for consent before touching a patient.
Tone of voice
The tone of voice that healthcare providers use can convey a range of emotions, from empathy and concern to frustration and impatience. Using a calm and reassuring tone can help to create a more positive and supportive environment.
Gestures
Gestures are another important aspect of nonverbal communication in healthcare settings. Patients may use gestures to express themselves when they are unable or unwilling to do so verbally.
Understanding the meaning behind common gestures is important for healthcare professionals. For example, a patient who is crossing their arms may be expressing defensiveness or discomfort, while a patient who is nodding their head may be indicating agreement or understanding.
Gestures can also signal pain or discomfort. For example, a patient who is rubbing their back or holding their chest may be experiencing pain, while a patient who is rubbing their temples or closing their eyes may be experiencing a headache.
It is important for healthcare professionals to respond appropriately to different gestures. For example, if a patient is expressing discomfort through their gestures, healthcare professionals may need to adjust their treatment plan or offer pain relief measures.
In addition, healthcare professionals should be aware of their own gestures and how they may be perceived by patients. For example, leaning forward can indicate interest and engagement, while crossing arms can indicate defensiveness or disinterest.
By understanding and interpreting gestures, healthcare professionals can improve communication with their patients and provide more effective care.
Nonverbal gestures, such as pointing or shaking the head, can help to reinforce verbal communication and provide clarity. However, healthcare providers should be aware of cultural differences in gestures and avoid using gestures that could be misinterpreted.
Proximity
The distance between healthcare providers and patients can convey different messages. Standing too close can be intimidating, while standing too far away can create a sense of disconnection. Finding a comfortable proximity can help to establish a positive rapport.
Mirroring
Mirroring a patient’s body language, such as leaning forward or nodding in agreement, can help to establish trust and build rapport. It shows that the healthcare provider is listening and understands the patient’s perspective.
Microexpressions
Microexpressions are brief facial expressions that can reveal underlying emotions or attitudes. Healthcare providers who are skilled in reading microexpressions can gain valuable insights into their patients’ needs and emotions.
Silence
Silence can be a powerful communication tool, especially in healthcare settings. Allowing patients time to process their thoughts and emotions can help to create a more supportive and empathetic environment.
Physical appearance
Healthcare providers who dress professionally and maintain good personal hygiene can convey a sense of competence and professionalism. However, it’s important not to place too much emphasis on physical appearance, as it can be a source of anxiety or insecurity for some patients.
What is the most powerful body language cues?
The most powerful body language cue in healthcare and in general is eye contact. Eye contact is a powerful nonverbal cue that can convey a wide range of emotions, including empathy, interest, concern, and understanding. It can help to establish trust and build rapport between healthcare providers and patients, and it can also be used to communicate respect and attentiveness in social situations.
When healthcare providers make eye contact with their patients, it shows that they are engaged and interested in the patient’s well-being. It can also help to put patients at ease and create a more relaxed and comfortable environment. Conversely, avoiding eye contact or looking away frequently can convey disinterest or lack of engagement.
Overall, eye contact is a powerful communication tool that can be used to convey a wide range of emotions and attitudes. In healthcare settings, it can be especially effective in building trust and rapport between healthcare providers and patients, and it can also help to improve patient outcomes by creating a more supportive and empathetic environment.
Detecting inconsistencies between verbal and nonverbal cues
Detecting inconsistencies between verbal and nonverbal cues is an important skill for healthcare professionals. Patients may not always express themselves clearly, and inconsistencies between verbal and nonverbal cues can indicate that a patient is not being entirely truthful or is experiencing emotional distress.
One common example of inconsistency is when a patient smiles or uses a light tone of voice while expressing pain or discomfort. In such cases, healthcare professionals should take note of the inconsistency and ask follow-up questions to better understand the patient’s true condition.
Other signs of inconsistency can include avoiding eye contact, fidgeting, or adopting a closed body posture while expressing confidence or assurance. In some cases, patients may also provide conflicting information, such as reporting different symptoms or giving different accounts of their medical history.
When healthcare professionals detect inconsistencies, it is important to approach the patient with empathy and compassion. Asking open-ended questions, acknowledging the patient’s concerns, and actively listening to their responses can help to build trust and encourage the patient to share their true thoughts and feelings.
In some cases, inconsistencies may also be a sign of deeper emotional distress or mental health issues. In these cases, healthcare professionals should approach the patient with sensitivity and refer them to a mental health professional if appropriate.
Overall, detecting inconsistencies between verbal and nonverbal cues is an important skill for healthcare professionals. By paying close attention to nonverbal cues and responding appropriately, healthcare professionals can provide more effective care and build stronger relationships with their patients.
In conclusion
nonverbal communication is a critical aspect of healthcare settings, and being able to accurately read and interpret body language can help healthcare professionals better understand their patients’ needs and emotions. By paying attention to common nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, gestures, and posture, healthcare professionals can gain valuable insights into their patients’ mental and physical states. By learning how to read and interpret these cues correctly, healthcare professionals can improve patient care and build stronger, more trusting relationships with their patients. So, if you’re a healthcare professional looking to enhance your communication skills, we encourage you to explore the fascinating world of nonverbal communication and learn how to read body language like a pro.
